Violin Concerto (“To the memory of an angel”)
——
Igor Stravinsky (1882-1971)
Itzhak Perlman, Violin
Boston Symphony Orchestra, Seiji Ozawa – Conductor
Recorded in 1980 (Deutsche Grammophon)
ONE-SENTENCE REVIEW:
Itzhak rules!
ORIGINAL LINER NOTES (by Volker Scherliess – translation by John Coombs):
If it is true that a recording can be not only entertaining but at the same time revealingly instructive, then that is the case here; it brings together two works of the same genre and the same period; each commissioned by a prominent violinist and composed with his particular technical accomplishments in mind – two virtuoso concertos, therefore, successors to the great bravura pieces of the 19th century, but by no means restricted to demonstrating dazzling violin playing.
Each is, indeed, a work of the highest quality, and occupies a place of importance in the oeuvre of its composer.
(Alban Berg once remarked that a concerto is the “art form in which it s not only the soloists who have an opportunity to display their virtuosity and brilliance, but also for once the composer.”)
The list of similarities could be extended further, but the remarkable fact is that these external resemblances highlight all the more clearly the fundamental contrast between the two works, and between their composers.
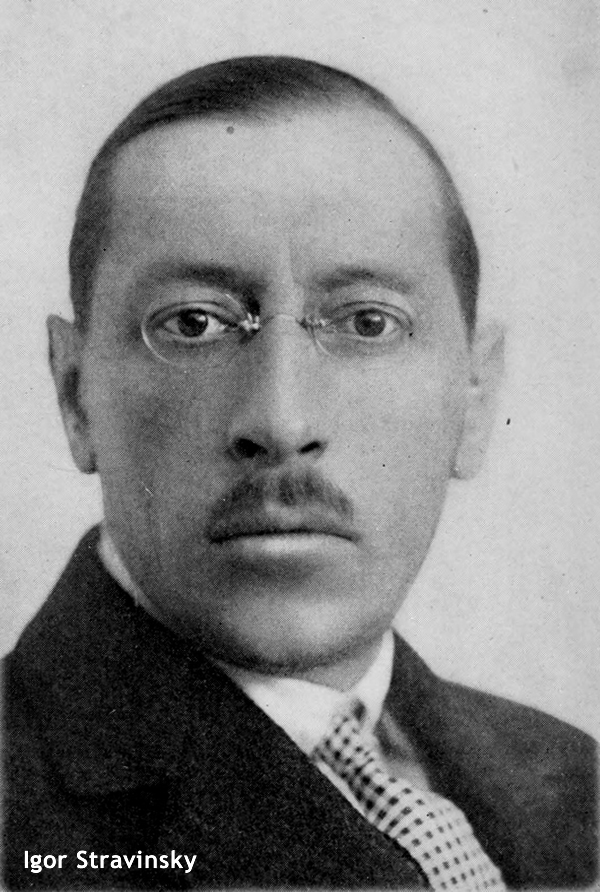 Stravinsky’s Concerto was written in 1931 for the young American violinist Samuel Dushkin, who (as is specifically stated in the score) gave the composer technical advice on the writing of the solo part.
Stravinsky’s Concerto was written in 1931 for the young American violinist Samuel Dushkin, who (as is specifically stated in the score) gave the composer technical advice on the writing of the solo part.
Stravinsky said, jokingly, that the Concerto should “smell of the violin,” and in the event no potential of violin technique remained unexploited.
The element of display is also fascinating in the orchestra, which despite its full scoring always creates the transparent effect of chamber music.
This work is a masterly example of neoclassicism, not reactionary and content with superficial stylistic copies, but creating something wholly new as a result of an affectionate approach to models from the past – often parodistically distorted.
The movement titles indicate a return to baroque forms: Toccata and Capriccio – two fast movements charged with motor energy – enclose Aria 1 and Aria II, both of which are dominated by a richly decorated cantabile line.
At the beginning of each movement the soloist plays the same motto-like chord D’ – E” – A”’, but otherwise the music is not concerned with thematic associations, with evolution from a germ cell or with rising to emphatic climaxes, but with assembling colorful elements in the manner of a collage.
The deliberate avoidance of subjective moods, expression and feelings, instead the creation of music which is refreshingly serene, effervescent and objective, music without a “message” or “idea” (except that of virtuosic playing) – that was Stravinsky’s intention.
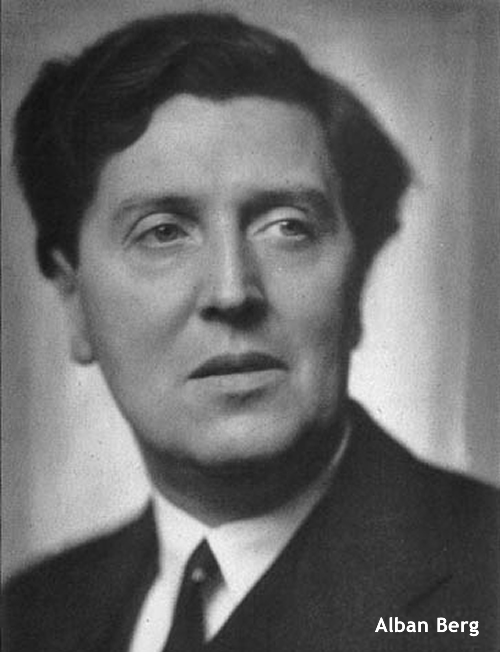 It was quite otherwise with Alban Berg.
It was quite otherwise with Alban Berg.
When the violinist Louis Krasner asked him for a violin concerto in February 1935, he was uncertain at first of the form which the work should take.
The death of the eighteen-year-old Manon Gropius, daughter of the brief marriage between Mahler’s widow Alma Mahler-Werfel and the architect Walter Gropius, on April 22 affected him so profoundly that he decided to create a memorial to the girl: he dedicated this Concerto “to the memory of an angel.”
Its layout encompasses several musical layers. Berg based his compositional procedure on Schoenberg’s twelve-note technique, but he used it in an unorthodox manner (his based 12-note row contains major, minor and whole-tone elements), and even combined it with purely tonal music – a Carinthian folk song and the chorale Es is genug in Bach’s harmonization.
These contrasting elements serve Alban Berg’s wish “to translate characteristics of the young girl’s nature into musical terms”: the Concerto as a whole is intended to depict life (1st movement), the struggle with death, and transfiguration (2nd movement).
When at the end a vision of the “angel” is evoked again by the reappearance of its musical motifs, the rare mastery with which Berg blended form and expression, musical logic and a poetic idea, is more than ever apparent.
TRACK LISTING:
- 1-2: Berg: Violin Concerto (“To the memory of an angel”)
- 3-6: Stravinsky: Violin Concerto
FINAL THOUGHT:
Not a great recording from a technical standpoint – it was the early days of CD production after all (either that or my CD is wearing out) – but the fantastic playing of Itzhak Perlman overcomes any technical issues and makes this a truly fantastic disk. The Stravinky almost feels like you’re listening to something as accessible as Mozart after hearing the 12-tone complexities of the Berg piece.
 Emily Sachs – President – Manka Music Group (A division of Manka Bros. Studios – The World’s Largest Media Company)
Emily Sachs – President – Manka Music Group (A division of Manka Bros. Studios – The World’s Largest Media Company)