Johannes Brahms (1833-1897)
The String Quintets
Quintet No. 1 in F Major, Op. 88
Quintet No. 2 in G Major, Op. 111
Produced by Gary Schultz
Recording Engineer: Charles Harbutt
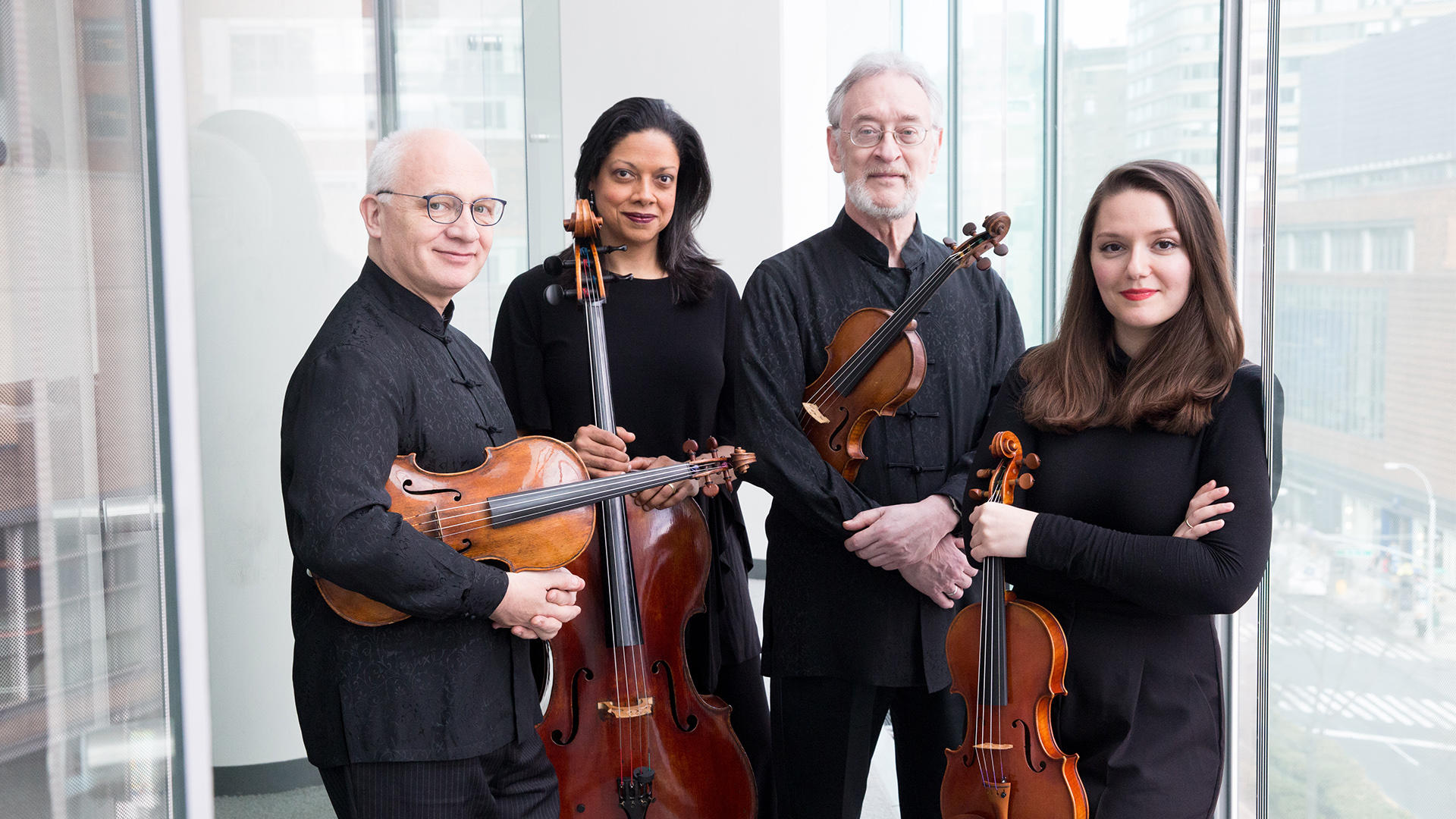
Julliard String Quartet (Robert Mann & Joel Smirnoff, Violins; Samuel Rhodes, Viola; Joel Krosnick, Cello) & Walter Trampler, Viola
Recording Location: Troy Savings Bank Music Hall, Troy, NY, May 15-17, 1995.
ONE-SENTENCE REVIEW:
These rarely-played chamber gems get the “Julliard” treatment to gorgeous effect but… actually, well-played doesn’t mean… exciting.
ORIGINAL LINER NOTES (Bruce Adophe, 1996):
Fifty years ago, in 1946, the Julliard String Quartet was formed by the 26-year-old Robert Mann, fresh out of the Army. Fifty years before that, in 1896, the 63-year-old Johannes Brahms, despondent over the recent death of Clara Schumann, composed Four Serious Songs (Op. 121) and Eleven Chorale Preludes (Op. 122).
Brahms, who died at 64, lived almost into the twentieth century. Although typecast as a forever-bearded Romantic god trapped in a remote pantheon called “The Three B’s,” the real Johannes Brahms was only a grandfather away from the generation that founded the original Julliard String Quartet.
Brahms is known to have said, “If we cannot write as beautifully as Mozart and Haydn, let us at least write as purely.” The comment discloses Brahms’ neoclassical bent and surely would have been taken as an anti-Wagner, anti-Liszt sentiment.
Liszt’s music was so utterly disliked by Brahms and Joseph Joachim (the great violinists who was the composer’s lifelong champion and sometime friend) that they used the word “lisztisch” to mean “damnable” in their letters.
In his String Quintet in F Major, Op. 88, composed in 1882, Brahms achieves a purity of form, voice-leading and counterpoint, which heralds a master composer in his maturity. The quintet opens with luminous nobility.
This quite soon gives way to a radiant, more intimate theme (related by the viola) clothed in a new key and a stunning new texture which no one but Brahms ever dreamed of: each instrument has its own special light – cello and second violin play pizzicato, but the cello divides the measure in two while the second violin plucks in six; the first violin plays eight notes to the bar while the first viola plays the tune in syncopated sixes; the remaining viola plays a counter-melody in four.
This kind of innovative rhythmic and textural design is a blueprint for much music of our century, suggesting even the polyrhythmic configurations of Elliott Carter (whose quartets the Julliard String Quartet has recorded). But the intricate musical web vanishes – before its complexity can register in the mind – into a simpler heartbeat patter, full of yearning.
The musical purity Brahms reverered is now clearly manifested as he explores these textures throughout the movement with mastery and deep feeling.
The dark, strring Grave ed oppassionato has enough solid mass to warrant an entire movement, yet Brahms employs it as a standard by which to discover the specific gravity of an Allegretto vivaco and a Presto.
These startling juxtapositions – and their subtle harmonic interrelatedness – seem to have been inspired by Beethoven, who, especially in his late string quartets, discovered uncharted areas of human expression through the investigation of extreme contrast. The underlying metaphor is that of our ultimate aloneness (Grave) in the midst of the busy world (Allegretto vivace and Presto).
The Beethoven connection can also be heard in the finale, which opens with two abrupt, stabbing chords in the manner of Beethoven’s string quartets Op. 59, No. 2, and the third movement of Op. 131.
Following the Beethovenian path still further, Brahms unfolds an uplifting fugue, announcing each entrance with those knifelike chords. Beethoven would not have rolled over but rather sat up straight (both images are problematic!) upon hearing Brahms’ tribute.
While the integration of fugue into sonata form conjures up Beethoven, fugal writing itself summons the spirit of Bach. When Brahms died, Joachim told the Neuen Freien Presse, “On the topmost peak stands Bach, the all-powerful, the incomparable, the creator, the great beginning. Mozart follows as the originator of new forms of beauty, and then comes – Brahms.”
The interviewer asked, “And Beethoven?” Joachim then firmly placed Brahms ahead of Beethoven.
In 1996 – as the new millennium approaches – we can understand the anxiety and exhilaration, the astounded concurrence of old and new, which accompanied the turn of the last century.
Claude Debussy, the prophet and pilot of musical modernism, was twenty-eight years old when, in 1890, Brahms composed the Quintet in G Major, Op. 111. It was the year that the Manhattan Building, the first entirely steel-frame building in the world, was erected in Chicago. At sixteen stories, it was (briefly) the world’s tallest building, earning the nickname “Hercules.”
Feeling the shifting winds, Brahms included a message with the manuscript of the quintet when he sent it to his publisher, Fritz Simrock: “With this letter you can bid farewell to my music – because it is certainly time to leave off…”
But the flowing Herculean architecture of Brahms’ Op. 111 Quintet will surely outlast Chicago’s steel-framed edifices. In fact, far from giving the impression that its composer might soon retire, the opening of the G-Major Quintet explodes into existence with a skyscraper of a first theme in the cello, set against a tempest in the remaining four instruments.
Brahms considered rewriting this opening passage to decrease the risk of the solo cello being drowned out. A draft exists in which the upper strings alternate their activity with rests, cutting the massive texture in half. The composer quickly returned to the original conception of the work, deciding that the rewrite sounded flimsy.
Brahms did not always want cellists to be heard, however. In a now famous story, Brahms was playing his own F-Major Cello Sonata with an unsatisfactory partner. The composer let loose at the piano with an enormous fortissimo, causing the cellist to shout over the music, “Maestro, I can’t hear myself at all,” to which Brahms countered, “Lucky for you!”
Brahms loved a full sound and was renowned for his rich, massive tone on the piano. The Julliard Quartet’s Robert Mann remembers a story once told by a musician whose father, many years earlier, had taken him to hear Brahms play his F-Minor Piano Quintet. The boy’s father leaned over just before the music started and whispered to his son, “Listen well to the strings in the opening unison passage because that will be the last time you can hear them at all!”
A friend of Brahms suggested to the composer that the high spirits in the Op. 111 Quintet may have been partially inspired by a public park in Vienna, known as the Prater. “You guessed it!” answered Brahms. “And the delightful girls there.”
If Brahms meant this last comment seriously, he would probably have been referring to the graceful second theme in the first movement, which beings in the violas and is soon passed to the violins – it is as fetching and enchanting a melody as any ever composed.
Brahms professed that his beautiful themes came to him in “instantaneous flashes,” which “quickly vanished,” sometimes before he could capture them on paper. He believed that “the themes that will endure in my music all appear to me in this way.”
Brahms did not mean that he was unconscious when composing, but that he experienced what he called a “semi-trance condition.” Explaining this concept to Joachim, Brahms stated, “You must realized that Milton, Shakespeare, Tennyson, Bach and Beethoven never wholly lost consciousness when they entered that border state.”
Of his own semi-trances, Brahms explained, “I always have a definite purpose in view before invoking the Muse and entering into such a mood.” Brahms decried music which did not achieve a balance between the spirtual and the intellectual plains.
He criticized, for example, the composer August Bungert, whose work was immensely popular throughout Europe in the 1890s, for composing only with the conscious mind.
Brahms predicted such music would soon “go into oblivion.” (He seems to have been coorect so far, although an unexpected Bungert festival is always a possibility given the current craze for thematic programming.)
There is certainly no shortage of inspired, entrancing melody in this quintet. In the Adagio, Brahms unveils another jewel – a sweet, sorrowful melody which abides sublimely on the first viola before the first violin appropriates it permanently.
The violin reveals three tragic visions of the theme (as opposed to the viola’s one). The viola makes a moving, cadenza-like plea towards the movements close, but the violins retain the poignant theme for a fourth and final utterance.
The Un poco allegretto ushers in another heart-stoppingly beautiful tune, this one quality prevails, giving way now and then to momentary disquiet. Here, and throughout this quintet, we find the Brahms so admired by Schoenberg for his ability to fully explore the complexity of a seemingly simple idea.
The five instruments are intricately engaged in imitative counterpoint that is rich without excess, at once elegant and luxurious.
The first viola seems to get an idea for the finale which the other instruments quickly realize is a good one. The Vivace ma non troppo presto takes the listener on a thrilling ride through the Hungarian countryside. It may seem brief, but you’ll find it is just the right length if you try dancing to it (which you’ll want to do).
By the way, it turns out that Brahms did not give up composing quite as soon as he had expected. Soon after completing this quintet, he heard the clarinetist Richard Muhlfeld play and suddenly found himself once again teeming with ideas, burning to compose.
TRACK LISTING:
Johannes Brahms – Quintet No. 1 in F Major, Op. 88
- Allegro non troppo ma con brio – 11:19
- Grave ed appassionato – Allegretto vivace Tempo 1 – Presto – Tempo 1 – 10:53
- Allegro energico – Presto – 5:32
Johannes Brahms – Quintet No. 2 in G Major, Op. 111
- Allegro non troppo, ma con brio – 12:48
- Adagio – 6:26
- Un poco allegretto – 6:13
- Vivace ma non troppo presto – 5:00
FINAL THOUGHT:
Normally, Brahms’ chamber music is a can’t-miss-bing-bang-bong success. But after listening to this disc… all I feel is… meh. The answer is ‘meh.’ Not terrible, it’s fine… but… ‘meh.’
 Emily Sachs – President – Manka Music Group (A division of Manka Bros. Studios – The World’s Largest Media Company)
Emily Sachs – President – Manka Music Group (A division of Manka Bros. Studios – The World’s Largest Media Company)